Recently, we found on the Quora forum that many users reported having their accounts banned due to abnormal activity detection after using a VPN to access social media platforms. Some professionals pointed out that most current platforms detect account anomalies through browser fingerprinting, and it is important to note that the key factor is browser fingerprinting rather than VPN.
So, what exactly are VPN and browser fingerprinting? What are the differences between them? And how can we effectively protect our accounts? Today, starting from the perspective of platform risk control mechanisms, we will analyze the real roles of browser fingerprinting and VPN, and provide you with the correct protection strategies.
1. What Is a VPN? Can It Really Protect Account Security?
A VPN is a type of network proxy tool whose main function is to hide and replace your real IP address. When you use a VPN, the website you visit will only see the IP address of the VPN server you selected, instead of your actual network location.
From a technical perspective, the main functions of a VPN include:
Hiding your real IP address
Changing your access region (country/city)
Encrypting network transmission to prevent traffic monitoring
Enhancing basic security in public network environments
In terms of its mechanism, when platforms identify VPN usage (via IP information), they can only see which IP address the request originates from and whether multiple accounts are logged in using the same IP. They cannot obtain much other useful data. Therefore, in modern platform risk control systems, IP is just one of the identification methods.
2. What Is Browser Fingerprinting?
Browser fingerprinting is one of the core technologies currently used by platforms to identify user identities. It is not something like cookies or account information, but a complete set of data synthesized from the browser and device environment, mainly related to your device information.
Common browser fingerprint parameters include:
Operating system type and version, CPU core count, memory size
Browser name, version, and kernel
Screen resolution and color depth, font list, time zone, and system language
WebGL/Canvas fingerprint, AudioContext fingerprint, and User-Agent
Browser plug-ins and API support status
For risk control mechanisms, comparing multiple accounts against a single parameter may lead to misjudgment. However, when dozens of parameters are combined to verify accounts, misjudgment is almost impossible.
3. Why Can Platforms Still Track You Even When Using a VPN?
1. IP Changes but Browser Fingerprint Remains the Same
A VPN can only change your IP address, but your browser, system, and hardware characteristics remain stable. From the platform's perspective, if the same browser fingerprint appears on IP addresses from multiple countries in a short period of time, this is considered high-risk behavior.
2. Platforms Prioritize Fingerprints Over IP Addresses
Modern risk control logic focuses more on device consistency, environment stability, and whether user behavior conforms to real user patterns. IP is just one of the reference signals, so taking excessive precautions on the IP front is not entirely effective.
3. Multi-Account Operations Expose Fingerprint Correlation
When multiple accounts use the same browser, have highly similar fingerprints, and exhibit consistent behavior patterns, platforms will directly determine them as associated accounts. At this point, a VPN is almost useless.
4. Core Differences Between Browser Fingerprinting and VPN
From the perspective of account security, we can understand the differences between the two as follows:
| Comparison Dimension | VPN | Browser Fingerprinting |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Function | Hides and replaces IP address | Identifies and distinguishes user device identities |
| Risk Level Addressed | Network source and geographic location | Account identity and device correlation |
| Uniqueness | No (shared by a large number of users) | Yes (highly unique) |
| Impact on Account Correlation Judgment | Minimal | Decisive |
| Ability to Prevent Account Bans Alone | No | Effective only when IP and environment are stable long-term |
| Support for Multi-Account Isolation | No | Yes |
| Alignment with Platform Risk Control Trends | Weight is gradually decreasing | Core identification method |
| Optimal Usage Method | Used in conjunction with a fingerprint browser | Used in conjunction with a VPN/proxy IP |
VPN and browser fingerprinting solve completely different problems. Although the protective effect of VPNs is no longer comprehensive, they still cannot be directly replaced. It is best to use both together.
5. The Real Role of Browser Fingerprinting in Account Security
A properly managed browser fingerprint environment mainly serves the following purposes:
Creating an independent device identity for each account
Preventing fingerprint correlation between accounts
Reducing the probability of being identified as an abnormal user by the system
Simulating an environment closer to that of real users
The goal of browser fingerprinting is not to hide the real information of your device, but to assign unique browser fingerprints to multiple accounts to prove their legitimate existence.
6. What Should We Do to Protect Our Accounts Securely?
From the perspective of risk control logic, if we can assign unique browser fingerprints to multiple accounts and use them in conjunction with appropriate VPN/proxy IPs, we can significantly enhance account security. This is currently the most reasonable and stable combination method.
The correct approach is: VPN/proxy IP provides a stable, clean, and region-appropriate network source, while browser fingerprint management ensures that each account has an independent, consistent, and long-term stable device environment. The combination of the two can simultaneously address risks at both the IP level and the identity identification level.
7. How to Implement Independent and Secure Browser Fingerprint Assignment?
To achieve this, we need to use a fingerprint browser, and the best option is the MostLogin Fingerprint Browser. Its main purpose is to run multiple customizable browser environments simultaneously, helping us quickly assign secure browser fingerprints to multiple accounts.
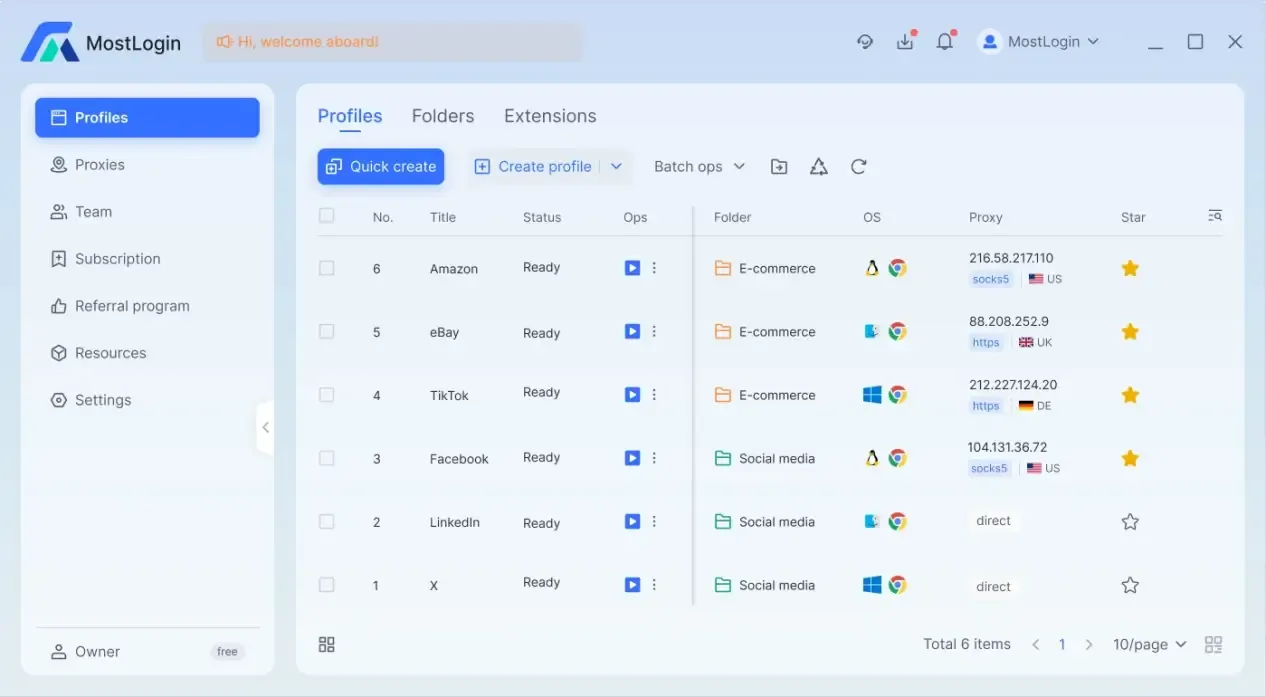
In addition to browser fingerprint configuration, the MostLogin Fingerprint Browser also supports importing proxies through various methods. It allows independent proxy configuration for each account/window, further enhancing account security.
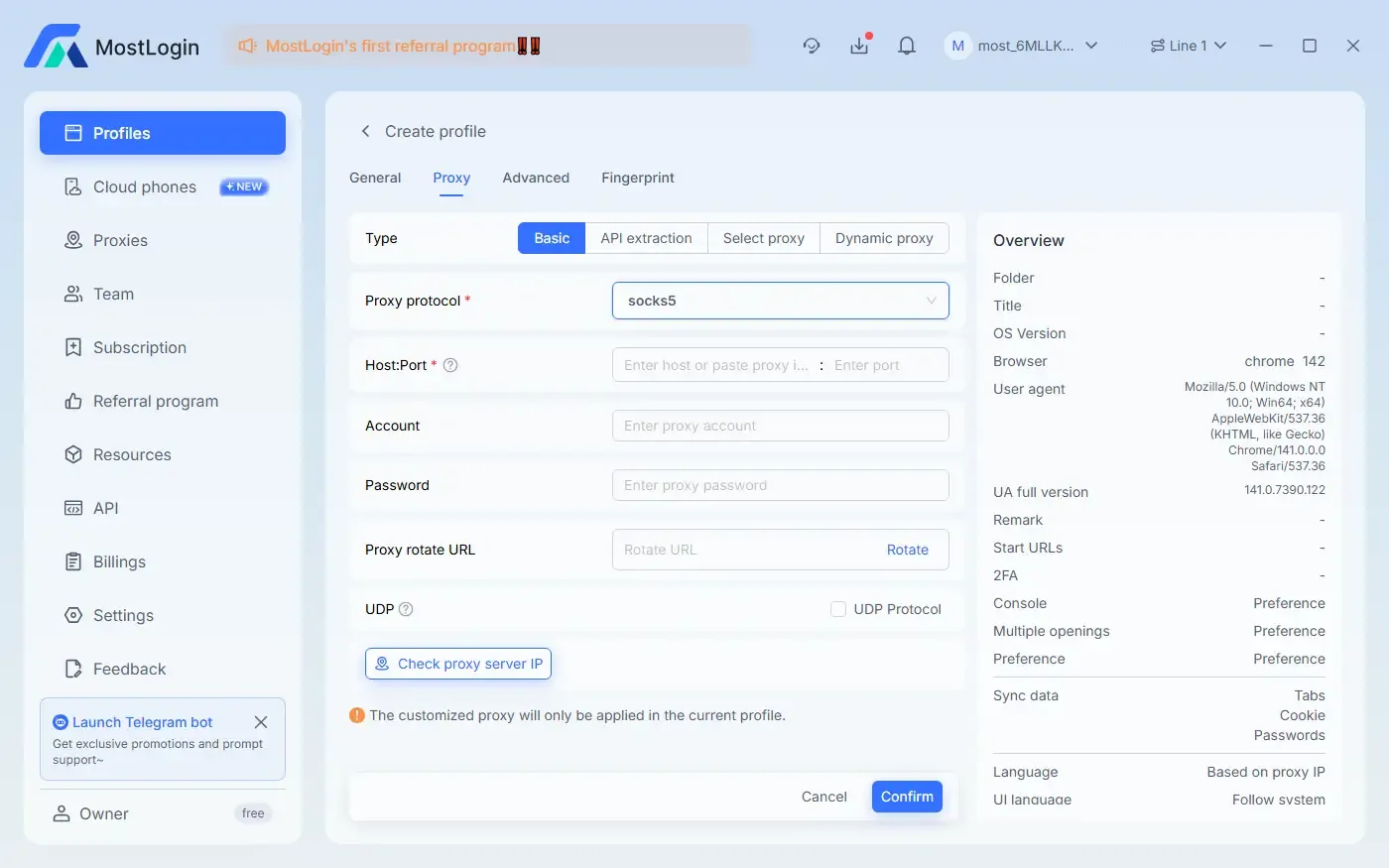
8. What Features Does the MostLogin Anti-Detection Browser Offer?
Reduces the risk of risk control and account bans: Fixed and authentic browser fingerprints can reduce issues such as abnormal logins, identity verification, and risk control reviews, improving account stability.
Prevents account correlation: Each account runs in an independent browser fingerprint environment, avoiding being identified as the same user by the system due to identical device, Canvas, WebGL, or font information.
Supports multi-account matrix operation: A single device can manage multiple accounts, with each account operating as if it were on a different real device, making it suitable for large-scale marketing and team collaboration.
Improves long-term account trust: A stable, consistent, and reasonable operating environment is useful for accumulating account weight and enhancing account credibility.
Simulates real regional users in conjunction with proxies: The fingerprint browser can bind an independent proxy IP to each account, ensuring that the account's region, network, and device environment remain consistent, making it more like real user operation.
Conclusion:
In the risk control systems of mainstream platforms today, IP is no longer the sole identification basis. Browser fingerprinting is the core factor that truly determines account security. A truly effective and long-term stable solution is to combine a stable and clean proxy IP with an independent and consistent browser fingerprint environment. This is currently the mainstream method for account security protection in the market.
Frequently Asked Questions
Why do accounts still get banned when only using a VPN?
Because a VPN can only change the IP address; platforms can still identify your real device through browser fingerprinting.
Is browser fingerprinting the same as cookies?
No. Cookies can be cleared, but browser fingerprints are generated from device and environment parameters and cannot be easily deleted.
Can one browser securely log in to multiple accounts?
No. Logging in to multiple accounts with the same browser fingerprint can easily trigger account correlation risk control.
Will browser fingerprints be detected as fake by platforms?
A reasonable, stable, and real-user-oriented fingerprint environment will not be identified as abnormal.
Which is more important, a VPN or a fingerprint browser?
Browser fingerprinting determines the underlying security of accounts, while a VPN only serves as an auxiliary tool. It is best to use both in combination.
Who is the fingerprint browser suitable for?
It is suitable for users engaged in multi-account operation, cross-border business, advertising, and those who need long-term stable accounts.
The MostLogin anti-detection browser tool helps users solve common problems such as multi-account operation, environment isolation, and account risk control.
For operational questions, please refer to the Official Help Documentation


