If you usually research content related to SSH and anti-detect browsers, we can generally guess that you are an advanced technical user who wants to make your network environment more secure or create an independent network environment. After all, for most people, ordinary proxies can meet many requirements. Although in some specific environments, there are indeed more detailed requirements for the network environment, some anti-detect browsers do not yet provide SSH proxy options.
Currently, most anti-detect browsers mainly use SOCKS5/HTTP(S) proxies. Today, we will give you a detailed explanation of how to use SSH in anti-detect browsers (this article only applies to anti-detect tools that natively support SSH or SSH Tunnel). If the browser you use will add SSH proxy options in the future, this article will still be applicable and useful.
We also have an article titled "Do Anti-Detect Browsers Support SSH? Professional Multi-Angle Analysis!". If you are interested, you can click the title to check it out.
What You Need to Prepare Before Starting
Before configuring SSH to an anti-detect browser, you need to prepare the following. These are common requirements on the market with no brand restrictions:
1. SSH Server
It can come from SSH Tunnel provided by proxy service providers, self-hosted VPS (Linux), internal corporate servers, public clouds (AWS, GCP, Alibaba Cloud, etc.). As long as it is standard SSH, it can be used.
2. Host (Server IP or Domain Name)
Their formats are generally similar to 123.45.67.89 or ssh.example.com. You may have one but just forgot; you can check if you have one by referring to such formats.
3. Port
The default SSH port is 22, but some service providers use other ports (such as 443, 8022) to enhance security. It is recommended to check the documentation first.
4. Username & Password
If your SSH uses password authentication, you need a Username and Password, which can also be set by yourself later.
5. Private Key (If Using Key Authentication)
Many people use key-based authentication. This type of login generally requires files in formats like .pem/.ppk/.key or a section of private key text. You can also check if you have one.
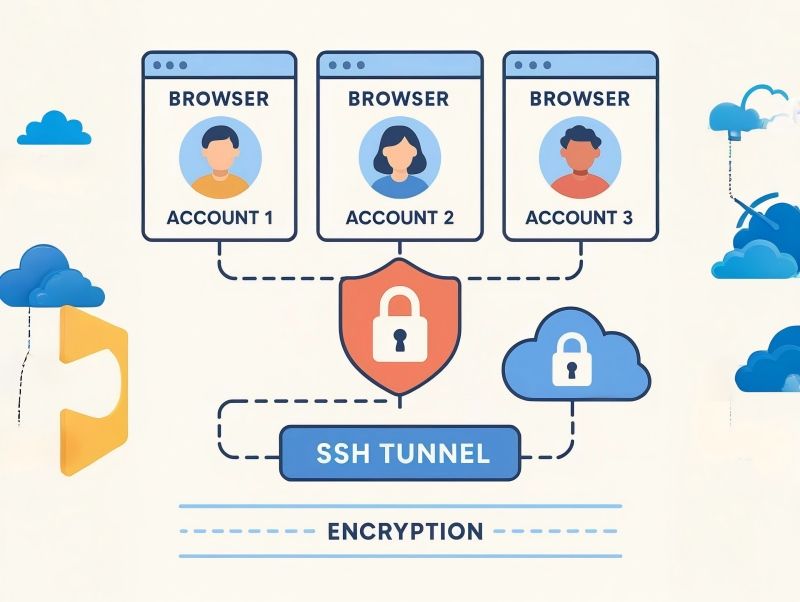
How to Use SSH as a Proxy?
SSH is essentially a remote login protocol, but it has very strong forwarding capabilities.
SSH Tunnel can do many things, such as encapsulating and encrypting your local browser traffic, forwarding it through a remote server, providing a new network exit, and completely isolating the environment. Many anti-detect browsers, in their early versions or some editions, provide options like: "SSH", "SSH Tunnel", "SSH Proxy". As long as you see these options, it means the software supports SSH proxy mode.
General SSH Configuration Steps
The following steps are applicable to anti-detect browsers that support SSH. If there is no corresponding option in your tool, it means it does not support it at least for now.
1. Open Network/Proxy Settings
It can usually be found in places like: "Network", "Proxy", "Browser Profile Settings", "SSH Tunnel".
2. Select SSH/SSH Tunnel Mode
Generally speaking, SSH/SSH Tunnel will be listed together with options like HTTP, HTTPS, SOCKS5. Just select SSH.
3. Enter Host and Port
For example: Host: 123.45.67.89, Port: 22 (I filled in 22 because it's the default, but not all ports are 22)
4. Enter Username/Password If Using Password Authentication
For example: Username: root, Password: ********
5. Upload Private Key If Using Key Authentication
Many high-security systems require uploading a .pem file or directly pasting the private key content. Generally, you also need to enter the Public Key Path and Key Password (if any) at this time.
6. Test Connection/Validate
Most tools will have a "Test Connection" or "Check" button. If the connection is successful, it will show prompts like "Connected", "SSH Tunnel Active", "Proxy running". If it fails, you need to check where the problem is.
Common SSH Connection Issues and Solutions
1. SSH Port Blocked by Firewall
This is because TCP port 22 is blocked in many regions. Solutions:
- Request the service provider to use an alternate port
- Use port 443 or 80
- Modify SSH configuration on the VPS
2. Permission Denied (Mismatched Public/Private Key)
This situation is definitely due to incorrect key permissions or format. Solutions:
- Use the correct key file
- Ensure private key permissions are: chmod 600 id_rsa on Linux
- Regenerate and bind the public/private key pair
3. Server Forwarding Function Not Enabled
In this case, SSH may not support proxy forwarding by default. Solution:
- Enable it in the server's /etc/ssh/sshd_config file, set AllowTcpForwarding to yes, then restart sshd.
4. Browser Traffic Not Actually Going Through SSH
Even if the connection is successful, the traffic may not actually go through the tunnel. Solutions:
- Check if "Use as proxy" is enabled
- Verify the exit IP on an IP detection website
- Check for DNS/WebRTC leaks
5. Connection Successful But No Internet Access
This problem is generally because the server does not have a gateway open, or the SSH Tunnel configuration is incomplete. If neither is the case, the service provider does not support this mode. Solutions:
- Contact the service provider
- Switch to a different SSH proxy
- Test with SOCKS5
When Should You Use SSH?
SSH has extremely high encryption strength and security, but there's no need to use it all the time or exclusively. Generally speaking, SSH is suitable for these situations:
1. High-security tasks, such as internal corporate systems, sensitive data operations, and strict privacy environments
2. You are familiar with Linux & SSH, and using it can be more flexible.
3. High requirements for traffic encryption. If your security requirements are much higher than ordinary ones, then SSH is indeed more suitable.
When Is SSH Less Recommended?
If your use cases include e-commerce store/cross-border operations, social media multiple accounts, advertising, SEO visitor simulation, and multi-environment independent browser businesses, SOCKS5 is still the most recommended. Compared with SSH, SOCKS5 is faster to configure, more stable, and more universal, and it is compatible with almost all anti-detect browsers. SSH is only suitable for a few high-end use cases, not daily multi-account use.
Final Words:
SSH is different from other proxy methods. If you want to use it when using an anti-detect browser, we hope the above methods and problem analysis can help you. Currently, more anti-detect browsers on the market do not support SSH proxies very well, so if you don't have such high requirements, it is recommended to use SOCKS5. Thank you for reading this far, and we hope you can solve your problem!
🚀 The Best Anti-Detect Browser - MostLogin
MostLogin anti-detect browser tool helps users solve high-frequency issues such as multi-account operation, environment isolation, and account risk control.
For operational questions, please refer to the official help documentation


